Tommer Leyvand
Currently Senior Director of Engineering at Apple, leading the Video Computer Vision (VCV) organization, a centralized applied research and engineering organization responsible for developing real-time on-device Computer Vision and Machine Perception technologies across Apple products.
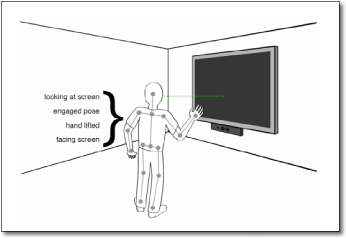
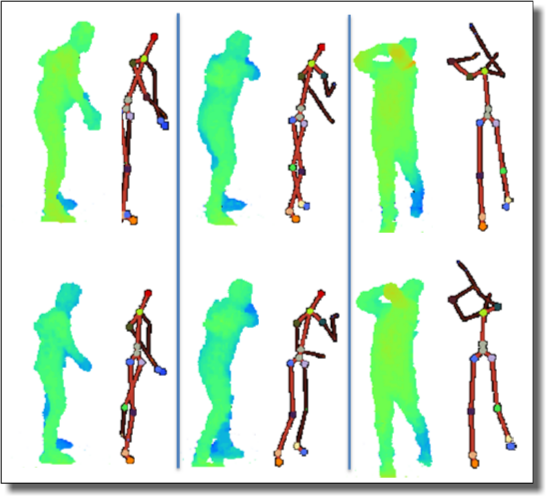
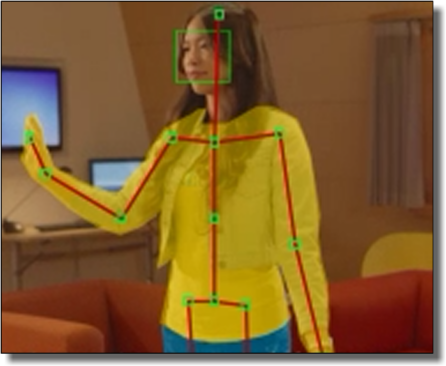
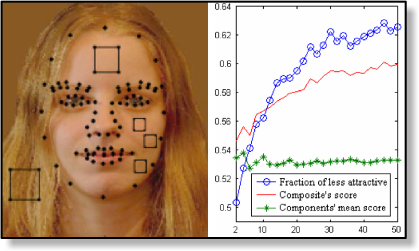
Previously leading the AI Camera group at Facebook, shipping Oculus Quest and Spark AR computer vision technologies. Prior to that at Microsoft leading software development at HoloLens and Kinect (Xbox 360, Xbox One and Windows).